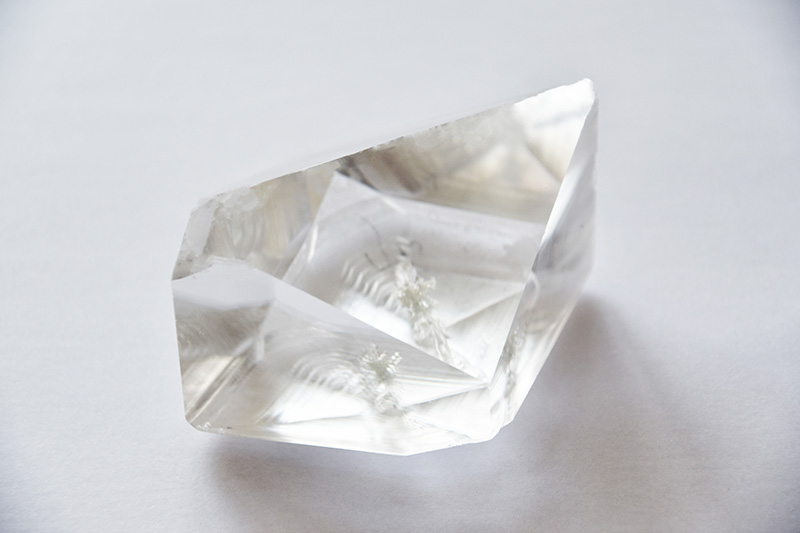
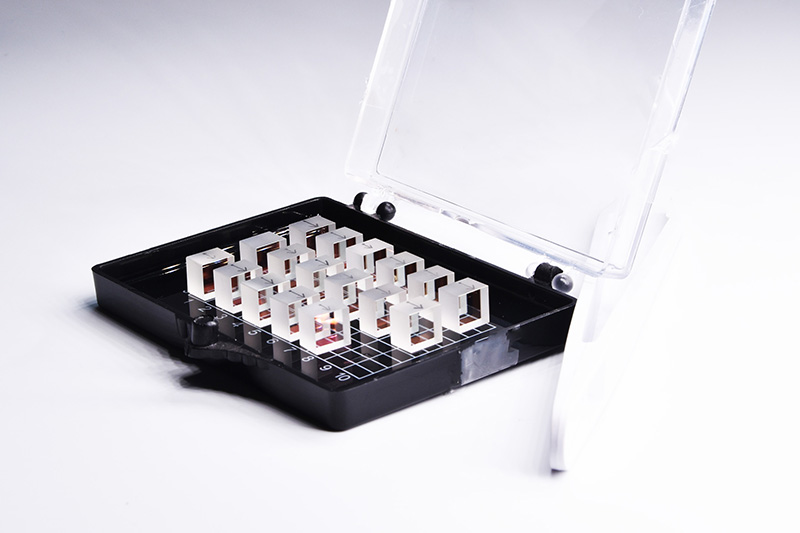
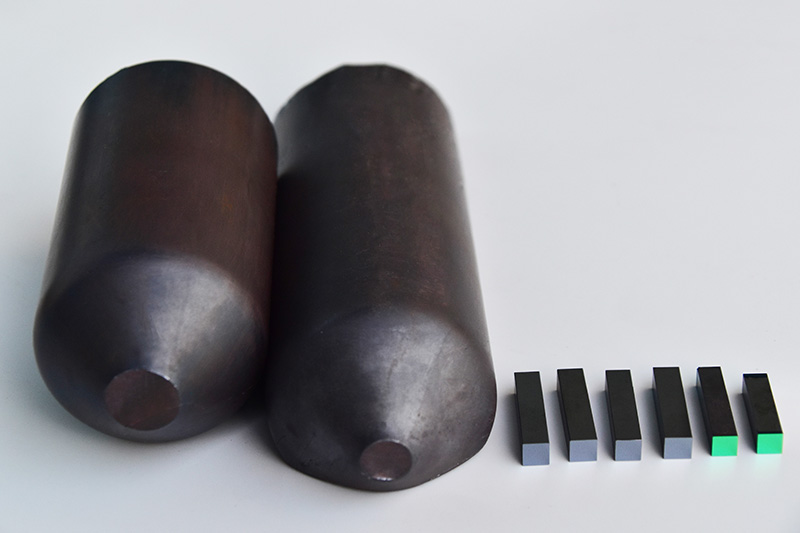
LBO Crystal
LBO (Lithium Triborate - LiB3O5) is now the most popularly used material for Second Harmonic Generation (SHG) of 1064nm high power lasers (as a substitute to KTP) and Sum Frequency Generation (SFG) of 1064nm laser source to achieve UV light at 355nm.
LBO is phase matchable for the SHG and THG of Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF lasers, using either type I or type II interaction. For the SHG at room temperature, type I phase matching can be reached and has the maximum effective SHG coefficient in the principal XY and XZ planes in a wide wavelength range from 551nm to about 2600nm. SHG conversion efficiencies of more than 70% for pulse and 30% for cw Nd:YAG lasers, and THG conversion efficiency over 60% for pulse Nd:YAG laser have been observed.
LBO is an excellent NLO crystal for OPOs and OPAs with a widely tunable wavelength range and high powers. These OPO and OPA which are pumped by the SHG and THG of Nd:YAG laser and XeCl excimer laser at 308nm have been reported. The unique properties of type I and type II phase matching as well as the NCPM leave a large room in the research and applications of LBO's OPO and OPA.
Advantages:
• Broad transparency range from 160nm to 2600nm ;
• High optical homogeneity (δn≈10-6/cm) and being free of inclusion;
• Relatively large effective SHG coefficient (about three times that of KDP);
• High damage threshold;
• Wide acceptance angle and small walk-off;
• Type I and type II non-critical phase matching (NCPM) in a wide wavelength range;
• Spectral NCPM near 1300nm.
Applications:
• More than 480mW output at 395nm is generated by frequency doubling a 2W mode-locked Ti:Sapphire laser (<2ps, 82MHz). The wavelength range of 700-900nm is covered by a 5x3x8mm3 LBO crystal.
• Over 80W green output is obtained by SHG of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser in a type II 18mm long LBO crystal.
• The frequency doubling of a diode pumped Nd:YLF laser (>500μJ @ 1047nm,<7ns, 0-10KHz) reaches over 40% conversion efficiency in a 9mm long LBO crystal.
• The VUV output at 187.7 nm is obtained by sum-frequency generation.
• 2mJ/pulse diffraction-limited beam at 355nm is obtained by intracavity frequency tripling a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser.
• A quite high overall conversion efficiency and 540-1030nm tunable wavelength range were obtained with OPO pumped at 355nm.
• Type I OPA pumped at 355nm with the pump-to-signal energy conversion efficiency of 30% has been reported.
• Type II NCPM OPO pumped by a XeCl excimer laser at 308nm has achieved 16.5% conversion efficiency, and moderate tunable wavelength ranges can be obtained with different pumping sources and temperature tuning.
• By using the NCPM technique, type I OPA pumped by the SHG of a Nd:YAG laser at 532nm was also observed to cover a wide tunable range from 750nm to 1800nm by temperature tuning from 106.5℃ to 148.5℃.
• By using type II NCPM LBO as an optical parametric generator (OPG) and type I critical phase-matched BBO as an OPA, a narrow linewidth (0.15nm) and high pump-to-signal energy conversion efficiency (32.7%) were obtained when it is pumped by a 4.8mJ, 30ps laser at 354.7nm. Wavelength tuning range from 482.6nm to 415.9nm was covered either by increasing the temperature of LBO or by rotating BBO.
| Basic properties | |
|
Crystal Structure |
Orthorhombic, Space group Pna21, Point group mm2 |
|
Lattice Parameter |
a=8.4473Å,b=7.3788Å,c=5.1395Å,Z=2 |
|
Melting Point |
About 834℃ |
|
Mohs Hardness |
6 |
|
Density |
2.47g/cm3 |
|
Thermal Expansion Coeficients |
αx=10.8×10-5/K, αy=-8.8×10-5/K,αz=3.4×10-5/K |
|
Thermal Conductivity Coefficients |
3.5W/m/K |
|
Transparency Range |
160-2600nm |
|
SHG Phase Matchable Range |
551-2600nm (Type I) 790-2150nm (Type II) |
|
Therm-optic Coefficient (/℃, λ in μm) |
dnx/dT=-9.3X10-6 |
|
Absorption Coefficients |
<0.1%/cm at 1064nm <0.3%/cm at 532nm |
|
Angle Acceptance |
6.54mrad·cm (φ, Type I,1064 SHG) |
|
Temperature Acceptance |
4.7℃·cm (Type I, 1064 SHG) |
|
Spectral Acceptance |
1.0nm·cm (Type I, 1064 SHG) |
|
Walk-off Angle |
0.60° (Type I 1064 SHG) |
| Technical Parameters | |
| Dimension tolerance | (W±0.1mm)x(H±0.1mm)x(L+0.5/-0.1mm) (L≥2.5mm)(W±0.1mm)x(H±0.1mm)x(L+0.1/-0.1mm) (L<2.5mm) |
| Clear aperture | central 90% of the diameterNo visible scattering paths or centers when inspected by a 50mW green laser |
| Flatness | less than λ/8 @ 633nm |
| Transmitting wavefront distortion | less than λ/8 @ 633nm |
| Chamfer | ≤0.2mm x 45° |
| Chip | ≤0.1mm |
| Scratch/Dig | better than 10/ 5 to MIL-PRF-13830B |
| Parallelism | better than 20 arc seconds |
| Perpendicularity | ≤5 arc minutes |
| Angle tolerance | △θ≤0.25°, △φ≤0.25° |
| Damage threshold[GW/cm2 ] | >10 for 1064nm, TEM00, 10ns, 10HZ (polished only)>1 for 1064nm, TEM00, 10ns, 10HZ (AR-coated)>0.5 for 532nm, TEM00, 10ns, 10HZ (AR-coated) |
Products categories
-

Phone
Phone
-
Email
Email
-

whatsapp
whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat

-

Top